So, you’ve heard the buzz about Bitcoin, but what information do you need to send/receive Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies?

The truth is that for beginners, the process of sending and receiving Bitcoin sounds like rocket science.
Fear not!
I’ve got your back, and I am here to unravel the mysteries of Bitcoin transactions in the simplest way possible. No complicated jargon, just plain, easy-to-understand English that will leave you feeling like a crypto pro in no time.
In this blog post, I’ll walk you through all the information you need to send/receive Bitcoin, ensuring that you have all the essential knowledge to confidently send or receive Bitcoin.
By the end of this article, you’ll not only understand how Bitcoin transactions work, but you’ll also have the confidence to start your own Bitcoin journey.
If you’re itching to learn and eager to take your first steps into the world of Bitcoin, keep reading.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital cryptocurrency, often referred to as “digital gold,” that was created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
It operates on a technology called blockchain, which is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers.
Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network, allowing users to send and receive payments without the need for intermediaries like banks.
The Basics of Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin transactions are at the heart of the cryptocurrency’s functionality.
They serve as how ownership and value are transferred between users on the Bitcoin network.
To grasp the information you need for sending and receiving Bitcoin, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of how these transactions work.
Overview of Bitcoin Transactions
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Unlike traditional financial systems, Bitcoin transactions occur directly between users without the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Decentralized Ledger: Transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of computers (nodes).
- Digital Signatures: Each transaction is digitally signed by the sender to prove ownership and ensure security.
Components of a Bitcoin Transaction
1. Input: This specifies the source of the funds being spent, typically referencing a previous transaction’s output.
2. Output: The destination where the funds are sent, usually in the form of a recipient’s Bitcoin address.
3. Amount: The quantity of Bitcoin being transferred from the input to the output.
4. Transaction Fee: To incentivize miners to include your transaction in the blockchain, you have to pay a small transaction fee.
Blockchain Confirmation
After a transaction is initiated, it is added to a pool of unconfirmed transactions.
Miners compete to validate and bundle these transactions into a new block on the blockchain through a process called mining.
Multiple confirmations (blocks added after your transaction) increase the security and irreversibility of your transaction.
What Information Do You Need To Send Bitcoin To Another Person
When you’re ready to send Bitcoin to someone else, you’ll need to gather specific information to complete the transaction accurately and securely.
Here’s a breakdown of the essential details you need:
1. Recipient’s Bitcoin Address
The recipient’s Bitcoin address is a long alphanumeric string (usually in the format of letters and numbers) where you want to send the Bitcoin.
It’s crucial to ensure the accuracy of the address, as errors can result in irreversible losses.
How to Obtain the Recipient’s Bitcoin Address:
Ask the recipient to provide their Bitcoin address.
Scan their QR code if they have one, which simplifies the process and minimizes the risk of errors.
2. Amount of Bitcoin to Send
Specify the exact amount of Bitcoin you wish to send to the recipient.
You can send a whole Bitcoin (1 BTC) or a fraction of it.
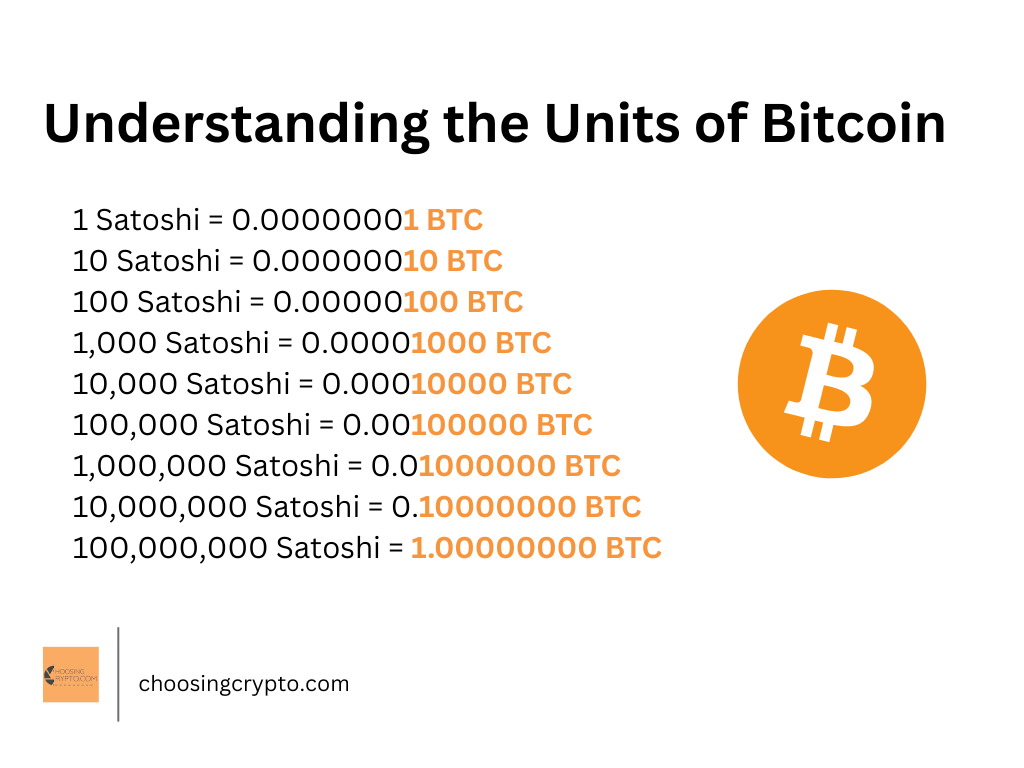
3. Transaction Fees
Bitcoin transactions often require transaction fees to incentivize miners to include your transaction in the blockchain.
The fee amount can vary depending on network congestion and transaction priority.
How to Determine an Appropriate Fee:
Most wallets provide fee estimation tools to help you choose an appropriate fee based on current network conditions.
You can customize the fee to prioritize speed or cost-efficiency.
Once you’ve gathered these details, you can initiate the Bitcoin transaction using your wallet’s interface.
Be sure to review the transaction details carefully, especially the recipient’s address, before confirming the transfer.
Mistakes in the recipient’s address are irreversible and can lead to the loss of your Bitcoin.
What Information Do You Need To Receive Bitcoin From Another Person
Receiving Bitcoin is a straightforward process, but it requires specific information to ensure the transaction is successful and secure.
Here are the key details you need when someone is sending Bitcoin to your wallet:
Your Bitcoin Address
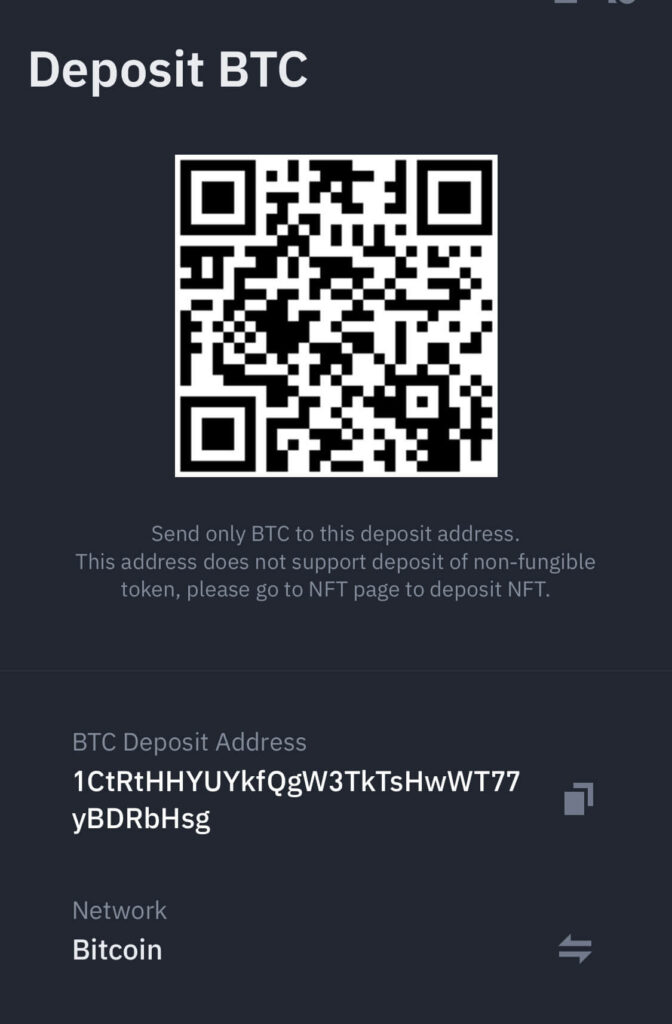
Your Bitcoin address is where others will send Bitcoin to you.
It’s a long alphanumeric string generated by your wallet, typically displayed as both the full address and a QR code for easy sharing.
The sender can scan this QR code with their wallet, eliminating the risk of address entry errors.
[READ: 5 Best Crypto Exchanges Where You Can Buy and Store Crypto]
What Is A Bitcoin Address
A Bitcoin address is a long string of letters and numbers, typically starting with a “1”, “3”, or “bc1” that serves as your identifier on the Bitcoin network.
It’s like your bank account number but for Bitcoin.
When you want to receive Bitcoin from someone, you share your Bitcoin address with them.
When someone sends Bitcoin to your address, it’s like depositing money into your Bitcoin account.
What Does A Bitcoin Address Look Like
Bitcoin addresses can look quite complex, but they follow a standard format.
Here’s what a typical Bitcoin address looks like:
Example of a Bitcoin address:
1BvBMSEYstWetqTFn5Au4m4GFg7xJaNVN2The image below will give you a clearer look at what a Bitcoin address looks like.
Key points to note about a Bitcoin address:
1. Length: Bitcoin addresses are usually 26-35 characters long.
2. Starts with “1”, “3”, or “bc1”: Bitcoin addresses can start with either a “1,” “3,” or “bc1.”
Each of these prefixes indicates a different address type:
- Addresses starting with “1” are known as P2PKH (Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash) addresses. They are the most common and have been in use since the early days of Bitcoin.
- Addresses starting with “3” are known as P2SH (Pay-to-Script-Hash) addresses. They are often used for more complex Bitcoin transactions involving scripts or multi-signature setups.
- Addresses starting with “bc1” are known as Bech32 addresses. These are Segregated Witness (SegWit) addresses, which offer some technical advantages like reduced transaction fees and improved security.
3. A mix of Letters and Numbers: Bitcoin addresses consist of a mix of uppercase letters (excluding “I” and “O” to avoid confusion with 1 and 0) and numbers. They are case-sensitive, so accuracy in entering the address is crucial.
How To Get A Bitcoin Address
Open your Bitcoin wallet or log into your crypto exchange account, be it Binance, Bybit, Kucoin, or any other exchange.
Look for the “Receive” or “Deposit Bitcoin” option.
You’ll see your Bitcoin address displayed as a QR code and as a text string.
You can copy and paste the text string when someone wants to send you Bitcoin.
[READ: A Detailed Guide on How to Get a Bitcoin Address]
Sending/Receiving Bitcoin Transactions in Practice
Now that you understand the basics of Bitcoin transactions, let’s delve into how to send/receive Bitcoin in practice.
Whether you’re sending Bitcoin to someone or receiving it, these step-by-step guides will help you navigate the process with confidence.
Sending Bitcoin:
1. Open Your Wallet: Open your Bitcoin wallet or exchange.
2. Verify Your Balance: Ensure you have a sufficient balance to cover the amount you intend to send, along with transaction fees. Otherwise, go here to see ways to buy Bitcoin.
3. Find the Send or Withdraw option: Look for an option like “Send” or “Withdraw.” This is the command that initiates the sending process.
4. Enter the recipient’s Bitcoin address: Obtain the recipient’s Bitcoin address. You can copy and paste the recipient’s Bitcoin address or scan their QR code.
5. Specify the Amount: Enter the exact amount of Bitcoin you wish to send to the recipient. Most wallets allow you to enter the amount in either Bitcoin or your local currency.
6. Transaction Fee: Decide on the transaction fee. Some Bitcoin wallets allow you to set transaction fees. You can typically choose from options like “low,” “medium,” or “high” fees, depending on how quickly you want the transaction to be confirmed.
7. Review the Details: Carefully review the recipient’s address, the amount, and the transaction fee to ensure accuracy.
8. Confirm the Transaction: Once you’ve verified all details, confirm the transaction.
9. Wait for Confirmation: After confirming the transaction, it will be broadcast to the Bitcoin network. Wait for confirmation to ensure the transaction is secure.
Receiving Bitcoin:
1. Open your Bitcoin wallet or exchange account.
2. Find the “Receive” or “Deposit Bitcoin” option.
3. Your wallet will display your Bitcoin address as a long string of characters or as a QR code.
4. Share your Bitcoin address with the sender. You can share this address in text form or by allowing the sender to scan the QR code.
5. Wait for the Transaction. Once the sender initiates the transaction, you’ll need to wait for it to be confirmed on the Bitcoin network.
6. Use Your Bitcoin. Once the transaction is confirmed, you can use your received Bitcoin for various purposes, including sending it to others, holding it as an investment, or making purchases with your Bitcoin.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Sending/Receiving Bitcoin
Sending and receiving Bitcoin can be challenging, especially for newcomers.
To help you safely manage your Bitcoin, here are some common mistakes to be aware of and avoid:
1. Mixing Up Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash Addresses
Bitcoin (BTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BCH) are two different cryptocurrencies with distinct addresses.
Ensure you use the correct address when sending or receiving funds to avoid loss.
2. Typing Errors When Entering Addresses
Manually entering long Bitcoin addresses can lead to errors.
Don’t forget that even a single incorrect character can send your Bitcoin to the wrong place.
So always double-check the address to avoid sending Bitcoin to the wrong destination.
3. Using Unsecure Wi-Fi Networks
Avoid conducting Bitcoin transactions on public Wi-Fi networks.
These networks may not be secure, making you more vulnerable to attacks.
Use a secure and private network when accessing your Bitcoin.
Dealing with Mistakes in Bitcoin Transactions
Mistakes can happen to even the most experienced Bitcoin users.
Whether you’ve sent Bitcoin to the wrong address or made an error in your transaction, it’s crucial to know how to address these situations.
Here’s a guide on dealing with common mistakes in Bitcoin transactions:
1. Sending to the Wrong Address: Oops!
Scenario: You’ve accidentally sent Bitcoin to the wrong address, and there’s no way to reverse the transaction.
What to Do:
First, don’t panic. Bitcoin transactions are irreversible by design, so there’s no “undo” button.
Contact the recipient (if known) and explain the situation. If it’s an honest mistake, they may return the Bitcoin to you.
In cases where you don’t know the recipient or they refuse to return the Bitcoin, there’s unfortunately little you can do.
Consider it a lesson in caution and always double-check addresses.
2. Unconfirmed Transactions: What to Do
Scenario: Your Bitcoin transaction is stuck as “unconfirmed” for an extended period, and you’re unsure what to do.
What to Do:
Unconfirmed transactions can happen when the network is congested or if you didn’t include an appropriate transaction fee.
Patience is key in this situation. Wait for some time, as the transaction may eventually get confirmed as miners process transactions with higher fees first.
If the transaction remains unconfirmed for an extended period (usually days), you can try using a service called “transaction acceleration” offered by some mining pools.
This may help push your transaction through.
3. Suspicious or Scam Transactions
Scenario: You suspect you’ve fallen victim to a scam or a fraudulent transaction.
What to Do:
If you believe you’ve been scammed or involved in a fraudulent transaction, gather as much information as possible, such as the Bitcoin address of the scammer.
Report the incident to your local law enforcement agency and any relevant financial regulatory authorities. If using a crypto exchange, report to them too.
And be cautious of potential scams in the future.
related;
- 7 Best Ways to Protect Your Bitcoin From Being Stolen
- Most Common Bitcoin Scams and How to Avoid Them
Conclusion
You’re now equipped with all the essential knowledge you need to send/receive Bitcoin confidently.
Remember, sending Bitcoin is as straightforward as knowing the recipient’s Bitcoin address and having a reliable wallet.
Receiving Bitcoin? Just share your Bitcoin address, and you’re good to go.
It’s like sending and receiving emails, but with digital gold!
So, whether you’re sending Bitcoin to a friend across the globe or receiving Bitcoin as payment for your latest masterpiece, remember, Bitcoin is more than just currency; it’s a revolution!
Embrace it, share it, and keep the crypto fire burning.
Additional Resources
To help you get better with Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies we have prepared additional resources below which we believe you will find useful.
But before you check them out, kindly visit our Instagram and Twitter pages, to join us for more content.
Additional Resources:
- What Exactly is Bitcoin and How Does it Work?
- How to Buy Bitcoin and Send It to Someone
- 4 Best Websites to Check Cryptocurrency Prices
- How People Make Money from Bitcoin
- Important Things to Know Before Buying Bitcoin
- How to Send Bitcoin Through a Bitcoin ATM
- How to Start Investing in Bitcoin as a Beginner
IMPORTANT; You must never send money to anyone you meet online asking to help you invest in cryptocurrency. They are scammers. Crypto is easy, and you can do it all by yourself.
DISCLAIMER:
The information provided here is intended for informational purposes only and should not be solely relied upon for making investment decisions. It does not constitute financial, tax, legal, or accounting advice. Additionally, I strongly recommend that you only invest in cryptocurrency an amount you are comfortable with potentially losing temporarily.
[READ: How Bitcoin Different from Money]