Get ready for a treat because we’ve got “10 Facts about Bitcoin” that will amaze you and make you wonder why you didn’t start exploring this digital treasure earlier.
Don’t worry if you’re new to cryptocurrencies – I’m here to explain it to you in plain and simple words.
No confusing tech stuff. Just the facts, explained in a way that anyone can grasp.
These facts will not only make Bitcoin less mysterious but also give you a strong foundation to begin your crypto journey.
And who knows, by the time you finish reading, you might be well on your way to becoming a Bitcoin pro!
Now, let’s dive in.
These 10 facts about Bitcoin will not only educate you but also entertain you.
So, let’s start our journey into the world of Bitcoin – it’s an exciting ride, and you’re in for an awesome adventure!
10 Facts about Bitcoin
These are the less-known facts about Bitcoin and trust me some of them will surprise you.
1. Bitcoin is not the first cryptocurrency
Contrary to what many people believe, Bitcoin was not the first cryptocurrency.
While Bitcoin is the most well-known and widely adopted cryptocurrency, several predecessors and early attempts at creating digital currencies existed before Bitcoin’s creation.
Here are a few notable examples:
1. DigiCash: DigiCash, created by David Chaum in the late 1980s, is often considered one of the earliest digital currencies. It aimed to provide digital cash with privacy features. While it was ahead of its time, DigiCash faced challenges with adoption and eventually filed for bankruptcy.
2. B-Money: In 1998, computer scientist Wei Dai proposed B-Money, a cryptographic system for anonymous, decentralized digital money. While B-Money never became a functional currency, it contributed to the conceptual development of cryptocurrencies.
3. HashCash: Created by cryptographer Adam Back in 1997, HashCash introduced the concept of proof-of-work (PoW) as a way to prevent email spam. Bitcoin later adopted PoW as its consensus mechanism.
4. Bit Gold: Nick Szabo proposed Bit Gold in 1998, which was a precursor to Bitcoin. Bit Gold incorporated elements of blockchain technology and decentralized currency. While it was never implemented, its ideas influenced the development of cryptocurrencies.
5. RPOW (Reusable Proof of Work): In the early 2000s, Hal Finney developed RPOW, a system that allowed users to exchange tokens generated through PoW. RPOW was one of the early experiments in digital currency.
Despite these early attempts, it was not until the publication of Satoshi Nakamoto’s whitepaper in 2008 and the launch of Bitcoin in 2009 that a successful, widely adopted cryptocurrency emerged.
Bitcoin’s innovative combination of blockchain technology, decentralized consensus, and a capped supply of coins set it apart and laid the foundation for the cryptocurrency ecosystem we know today.
[READ: The Minimum Amount to Start Investing in Bitcoin]
2. The last Bitcoin will be Mined in 2140
According to the Bitcoin protocol, the last Bitcoin is expected to be mined around the year 2140.
This is a fundamental aspect of Bitcoin’s design and monetary policy.
Here’s how it works:
1. Capped Supply: Bitcoin has a maximum supply cap of 21 million coins. This limit was hardcoded into the Bitcoin protocol by its creator, Satoshi Nakamoto. It is a key feature that distinguishes Bitcoin from traditional fiat currencies, which can be printed without limit.
2. Halving Events: To gradually approach the 21 million coin limit, Bitcoin experiences periodic halving events, which occur approximately every four years. During a halving, the reward that miners receive for adding new blocks to the blockchain is cut in half.
3. Halving Schedule: The initial reward for miners when Bitcoin was first launched in 2009 was 50 Bitcoins per block. The first halving event in 2012 reduced this reward to 25 Bitcoins. Subsequent halvings occurred in 2016 (12.5 Bitcoins per block) and 2020 (6.25 Bitcoins per block).
4. Predicted Timeline: Halving events will continue until approximately 2140, at which point the block reward will become so small that it effectively reaches zero. At this stage, miners will rely solely on transaction fees for their income, and no new Bitcoins will be created.
5. Scarcity and Value: The capped supply of 21 million Bitcoins is designed to create scarcity and is often cited as a reason for Bitcoin’s potential long-term value. As the supply of new Bitcoins diminishes, some believe that increased demand could drive up the price of existing Bitcoins.
3. First Bitcoin ATM was in Vancouver, Canada
The first Bitcoin ATM (Automated Teller Machine) was installed and operated in Vancouver, Canada.
This historic event took place in October 2013 and marked a significant milestone in the adoption and accessibility of Bitcoin.
Here are some details about the first Bitcoin ATM in Vancouver:
1. Operator: The first Bitcoin ATM in Vancouver was operated by a company called Robocoin, which was one of the early pioneers in the Bitcoin ATM industry.
2. Location: The Bitcoin ATM was located in Waves Coffee House, a popular café located in downtown Vancouver. This location was chosen to provide easy access to both local residents and tourists.
3. Functionality: The Bitcoin ATM allowed users to buy Bitcoin in Canadian dollars. Users could deposit Canadian currency into the machine and receive Bitcoin in their digital wallets.
4. Media Attention: The installation of the first Bitcoin ATM in Vancouver garnered significant media attention and brought Bitcoin into the mainstream spotlight. It was seen as a symbol of Bitcoin’s growing acceptance.
5. Subsequent Growth: Following the success of the first Bitcoin ATM in Vancouver, Bitcoin ATMs began to appear in various other cities around the world, making it easier for people to buy and sell Bitcoin in person.
[READ: How to Buy Bitcoin Using Bitcoin ATM]
4. The Pizza That Cost 10,000 Bitcoins

One of the most famous stories in the history of Bitcoin is the tale of the pizza that cost 10,000 Bitcoins.
This story highlights the incredible evolution of Bitcoin’s value and its journey from being virtually worthless to a valuable asset:
1. Pizza Day: On May 22, 2010, Laszlo Hanyecz, a programmer and early Bitcoin enthusiast, posted a request on a Bitcoin forum. He offered to pay 10,000 Bitcoins in exchange for two pizzas.
2. Bitcoin’s Early Days: At the time of the pizza transaction, Bitcoin had only been in existence for about a year. Its value was still highly uncertain, and it had not gained widespread attention or adoption.
3. Pizza Purchase: A fellow Bitcoin enthusiast took up Laszlo’s offer and ordered the pizzas for him. The transaction was completed successfully, and Laszlo received his two pizzas in exchange for the 10,000 Bitcoins.
4. Mind-Blowing Value Today: Fast forward to the present day, and the story of those two pizzas has become legendary. With the astronomical increase in Bitcoin’s value over the years, those 10,000 Bitcoins are now worth a mind-boggling sum. The value of Bitcoin has surpassed all expectations, making the pizzas one of the most expensive meals in history.
5. Bitcoin Pizza Day: The day of this historic pizza purchase “May 22”, is now celebrated as “Bitcoin Pizza Day” every year in the cryptocurrency community. It serves as a reminder of Bitcoin’s humble beginnings and the incredible journey it has undertaken since.
5. The Bitcoin Creator holds 1,000,000 Bitcoin
Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, mined approximately one million Bitcoins in the early days of the cryptocurrency, making it one of the largest individual holdings of Bitcoin.
However, the information about Satoshi’s holdings and activities is shrouded in mystery.
Satoshi Nakamoto disappeared from the public eye in 2010 and has not been heard from since.
The Bitcoins mined by Satoshi, often referred to as “Satoshi’s stash” or “Satoshi’s coins,” have never been moved or spent.
The untouched nature of these coins has fueled speculation and intrigue within the cryptocurrency community.
6. About 20% of Bitcoin has been Lost Forever
According to Chainalysis, a company that studies blockchain, about 20% of all the Bitcoin ever mined has either disappeared or is locked away in wallets that nobody can get into.
Most of these missing Bitcoins belong to folks who have passed away without telling anyone how to access their Bitcoin stash.
Others are from folks who’ve misplaced their private keys – the special codes needed to open Bitcoin wallets.
It’s important to note that Bitcoin wallets, whether they’re physical gadgets, computer programs, or even online services, don’t come with a “reset password” option.
So, if you lose your private key, you lose your Bitcoin.
It’s as simple as that!
That’s why lots of people new to cryptocurrencies often prefer to keep their coins on reputable crypto exchanges like Binance, Kucoin, Gate.io, or Bybit.
These exchanges offer a handy “reset password” feature in case you forget your login details.
7. Bitcoin is legal tender in El Salvador
El Salvador became the first country in the world to officially adopt Bitcoin as legal tender.
The Bitcoin Law, proposed by El Salvador’s President Nayib Bukele and approved by the country’s legislature, came into effect on September 7, 2021.
Here are some key points about this development:
1. Legal Tender: The Bitcoin Law declares Bitcoin as legal tender alongside the United States dollar, which was already the official currency of El Salvador. This means that businesses and individuals in the country must accept Bitcoin as a form of payment for goods and services, just as they would with the US dollar.
2. Currency Conversion: The law also stipulates that prices can be expressed in Bitcoin, but businesses must also provide a way for customers to convert Bitcoin to US dollars at the prevailing exchange rate, allowing them to choose their preferred form of payment.
3. Government Initiatives: The government of El Salvador has initiated various programs to facilitate the use of Bitcoin, including a government-issued digital wallet called “Chivo” that offers incentives to encourage adoption.
4. Infrastructure: El Salvador has worked to establish the necessary infrastructure for Bitcoin transactions, including Bitcoin ATMs, and plans to use volcanic energy for Bitcoin mining.
5. Reactions and Challenges: The decision to make Bitcoin a legal tender has sparked a range of reactions and challenges. Some have praised the move for its potential to increase financial inclusion and reduce the cost of remittances, while others have raised concerns about the potential risks and volatility associated with cryptocurrencies.
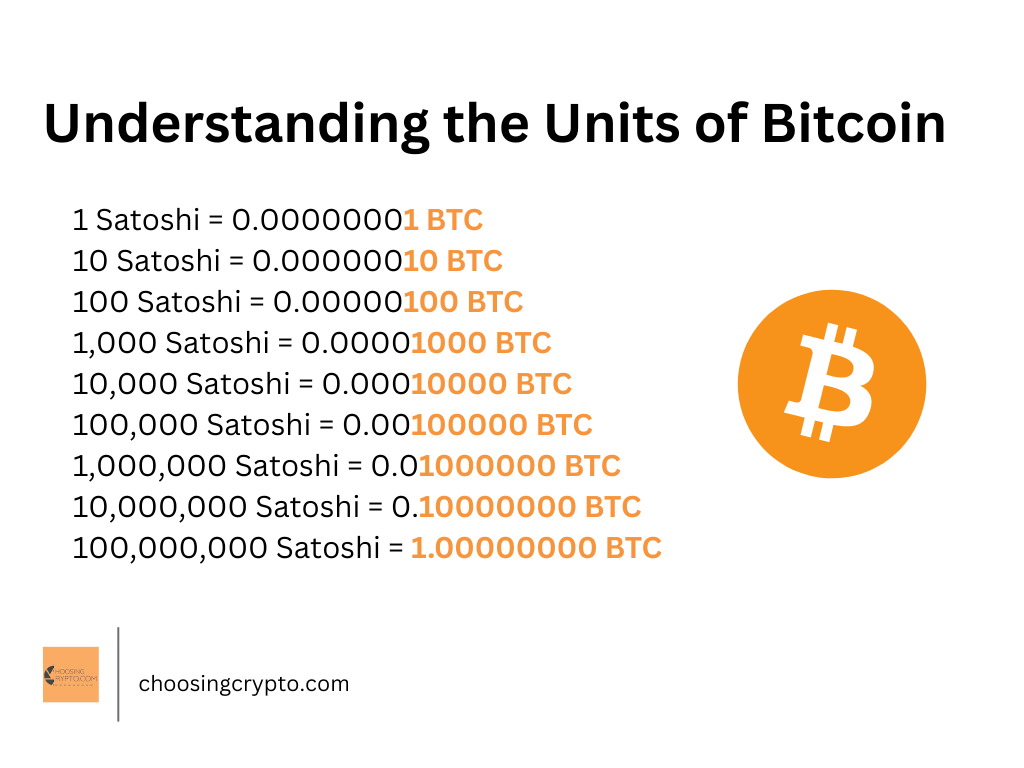
8. The smallest unit of a Bitcoin is Known as Satoshi
The smallest unit of a Bitcoin is known as a “Satoshi.”
It was named in honor of Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin.
One Bitcoin (BTC) can be divided into 100 million Satoshis (100,000,000 Satoshis).
This subdivision allows for more granular and precise transactions, especially as the price of Bitcoin has increased over the years.
For everyday transactions and microtransactions, the use of Satoshis is more practical than dealing with whole Bitcoins.
Here’s a breakdown:
1 Bitcoin (BTC) = 100,000,000 Satoshis (Sats)
So, if you were to send someone 0.001 BTC, you would be sending them 100,000 Satoshis (0.001 BTC * 100,000,000 Sats/BTC = 100,000 Sats).
Satoshi units are commonly used in discussions involving Bitcoin’s usability for everyday payments and in the context of Lightning Network, a second-layer scaling solution for Bitcoin, where micropayments are common.
9. Bitcoin Transactions are Traceable
Bitcoin transactions are traceable, they are not necessarily completely anonymous.
These transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is available for anyone to inspect.
Here’s how the traceability of Bitcoin transactions works:
1. Public Ledger: The Bitcoin blockchain is a decentralized and publicly accessible ledger that contains a record of all Bitcoin transactions. Each transaction is linked to the one before it and the one after it, forming a chain of blocks.
2. Transaction Addresses: Bitcoin transactions involve sending BTC from one wallet address to another. These addresses are alphanumeric strings that serve as pseudonyms for users. The addresses used in transactions are visible on the blockchain, but they are not directly tied to real-world identities.
3. Transaction Details: A Bitcoin transaction includes details such as the sender’s address, the receiver’s address, the amount of BTC transferred, and a digital signature. These details are recorded on the blockchain.
4. Blockchain Analysis: While Bitcoin addresses are pseudonymous, blockchain analysis tools and techniques can be used to trace transactions and potentially link them to real-world entities. Advanced analytics can help identify patterns, track funds, and infer connections between addresses.
5. Privacy Measures: To enhance privacy, some users employ best practices like using new addresses for each transaction, using privacy-focused coins, or using coin mixing services that obscure the source of funds.
10. The Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a second-layer scaling solution for the Bitcoin network.
It was created to address some of the challenges that Bitcoin faces, such as scalability and high transaction fees.
Here are some key points about the Lightning Network:
1. Scalability Solution: The Lightning Network is designed to increase the scalability of the Bitcoin network by enabling faster and cheaper transactions. It aims to alleviate congestion on the main blockchain.
2. Off-Chain Transactions: Lightning Network transactions are conducted off-chain, meaning they don’t need to be recorded on the main Bitcoin blockchain. This reduces the load on the blockchain and speeds up transaction processing.
3. Payment Channels: Lightning Network transactions are conducted through payment channels, which are like private channels between users. These channels allow users to send and receive Bitcoin without involving the main blockchain for every transaction.
4. Lightning Network Nodes: To use the Lightning Network, users need to set up Lightning Network nodes or use a wallet that supports Lightning. These nodes facilitate the routing of payments through the network.
5. Instant Transactions: Transactions on the Lightning Network are nearly instant, making them suitable for small, everyday transactions like buying coffee or paying for online services.
6. Reduced Fees: Lightning Network transactions typically have lower fees compared to on-chain Bitcoin transactions. This makes microtransactions and small-value transactions more cost-effective.
The Lightning Network represents a significant step in improving the scalability and usability of Bitcoin as a means of payment.
It allows for fast, low-cost transactions, making it a promising solution for the future of digital payments.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of “10 Facts about Bitcoin,” I hope you’ve found these nuggets of knowledge helpful in understanding this digital sensation.
As you keep exploring Bitcoin, remember these key points, and you’ll be all set to navigate the thrilling world of digital currency.
Keep in mind that while Bitcoin might seem a bit complicated at first, it’s a journey that’s definitely worth embarking on.
So, whether you’re interested in investing or just curious about Bitcoin, these 10 facts are your starting point on the path to becoming a savvy Bitcoin enthusiast.
Additional Resources
To help you get better with Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies we have prepared additional resources below which we believe you will find useful.
But before you check them out, kindly visit our Instagram and Twitter pages, to join us for more content.
Additional Resources:
- How to Start Investing in Bitcoin as a Beginner
- 7 Misconceptions about Bitcoin to Stop Believing
- What Exactly is Bitcoin and How Does it Work?
- 5 Best Bitcoin Exchanges to Use
- 7 Best Ways to Protect Your Bitcoin from Theft and Hacks
- Common Mistakes Crypto Investors and Traders Make
- 3 Best Stablecoins to Use

IMPORTANT; You must never send money to anyone you meet online asking to help you invest in cryptocurrency. They are scammers. Crypto is easy, and you can do it all by yourself.
DISCLAIMER:
The information provided here is intended for informational purposes only and should not be solely relied upon for making investment decisions. It does not constitute financial, tax, legal, or accounting advice. Additionally, I strongly recommend that you only invest in cryptocurrency an amount you are comfortable with potentially losing temporarily.
[READ: How To Choose a Crypto Exchange]
