Imagine a world where transactions are fully transparent, secure, and tamper-proof—all without relying on banks or governments. Sounds impossible? That’s exactly what blockchain technology makes possible.
If “blockchain” feels confusing, you’re not alone. When I first heard about it, terms like “decentralization” and “immutable ledgers” made it seem harder than it was.
But here’s the truth: blockchain isn’t just for tech experts or crypto enthusiasts. It’s a game-changing technology that anyone can understand with the right explanation.
That’s why I’m here—to break it down. In this post, you’re going to learn what blockchain is, how it works, and why it’s being called revolutionary.
New to crypto? I offer beginner-friendly 1-on-1 coaching, and your first session is free. Check it out here.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Imagine a digital book that anyone can read, but no one can edit or erase. That’s how blockchain works—a secure, transparent digital ledger for recording data across a network of computers called nodes.
Unlike traditional systems that rely on centralized databases, such as those used by banks, blockchain operates on a decentralized model. Instead of storing data in one place, identical copies are distributed across the network. This shared structure ensures everyone can access the same information, promoting transparency and trust.
What makes blockchain revolutionary is its tamper-proof design. Once data is added, it can’t be changed. Information is grouped into blocks, each connected to the next through a cryptographic hash—a unique digital fingerprint. These links form a chain of blocks—hence the term “blockchain.”
The security of the blockchain is extraordinary. To alter one block, you’d need to change every block in the chain across the entire network—an impossible task. Plus, its decentralized nature removes the need for a single controlling authority. Instead, the network’s participants collectively verify and manage the data, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
Think of each block as a page in this digital book. When a page is filled with records, it’s sealed, locked, and linked to the previous one. This connection keeps the data secure and unchangeable.
Blockchain is more than just technology. It offers a transparent, secure way to store and share data without central control. It powers innovations like cryptocurrencies and can potentially transform industries like finance and healthcare.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain securely records and verifies data through a clear, structured process. Let’s break it down:
1. Transaction Initiation
Chris wants to send Bitcoin to Tracey. To start, he enters Tracey’s wallet address and the amount to transfer. This action creates a transaction, which is then digitally signed using Chris’s private key. The digital signature proves that Chris is the true owner of the Bitcoin being sent and authorized the transfer.
2. Broadcasting to the Network
The signed transaction is sent to a decentralized network of computers, called nodes. These nodes play a crucial role in verifying and processing transactions. Once received, the transaction is placed into a temporary storage area called the mempool while it waits to be included in a block.
3. Validation
The nodes verify two important factors: whether Chris has enough Bitcoin for the transfer and if the transaction details are correct. They also check that the digital signature is valid and that the transaction has not been previously spent (double-spend prevention). To ensure legitimacy, the network relies on a consensus mechanism, such as Proof of Work (PoW), which involves miners competing to solve cryptographic puzzles, or Proof of Stake (PoS), which selects validators based on the amount of cryptocurrency they’ve staked and other network rules.
4. Block Creation
After validation, the transaction is grouped with other verified transactions to form a “block.” Each block contains:
- A list of transactions.
- A timestamp.
- A cryptographic hash linking it to the previous block.
- A unique cryptographic hash for the block itself, generated during the consensus process.
5. Adding the Block to the Blockchain
The new block is added to the existing chain of blocks, known as the blockchain, creating a secure, tamper-resistant sequence. This structure ensures data integrity across the entire network.
6. Completion
Once added, the transaction is finalized. Tracey receives the Bitcoin, and the blockchain updates across all nodes. This keeps everyone in the network up to date with the latest ledger version.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is changing the game with its unmatched security, reliability, and transparency. Let’s break down its key features in simple terms:
1. Decentralization
Blockchain runs on a global network of computers (nodes) instead of relying on a central authority like a bank. Each node has a full copy of the data, ensuring the system keeps running even if one fails. This decentralized structure boosts resilience, reduces corruption risks, and guarantees continuous operation.
2. Transparency
Every transaction on a blockchain is visible to the entire network. Once recorded, it’s permanent and accessible, like a public ledger that anyone can review but no one can alter. This openness builds trust and ensures accountability.
3. Immutability
Data on a blockchain cannot be changed or deleted. Transactions are linked using cryptography, creating a secure, unbreakable chain. This immutability protects records from tampering, ensuring they stay accurate and trustworthy.
4. Security
Blockchain uses advanced encryption to secure transactions. Its decentralized setup eliminates single points of failure, making it highly resistant to hacking. This makes blockchain a reliable choice for safeguarding sensitive information.
5. Efficiency and Automation
Smart contracts—self-executing programs—are a game-changer. They automate tasks based on set conditions, like releasing payments once goods are delivered. By removing intermediaries, smart contracts reduce costs, speed up processes, and minimize errors.
Struggling to understand how crypto/blockchain really works? I can guide you step-by-step.. Your first session is free. Start here.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Database: What’s the Difference?
Blockchain and traditional databases both store data, but they work in very different ways. Let’s compare them to see what sets blockchain apart.
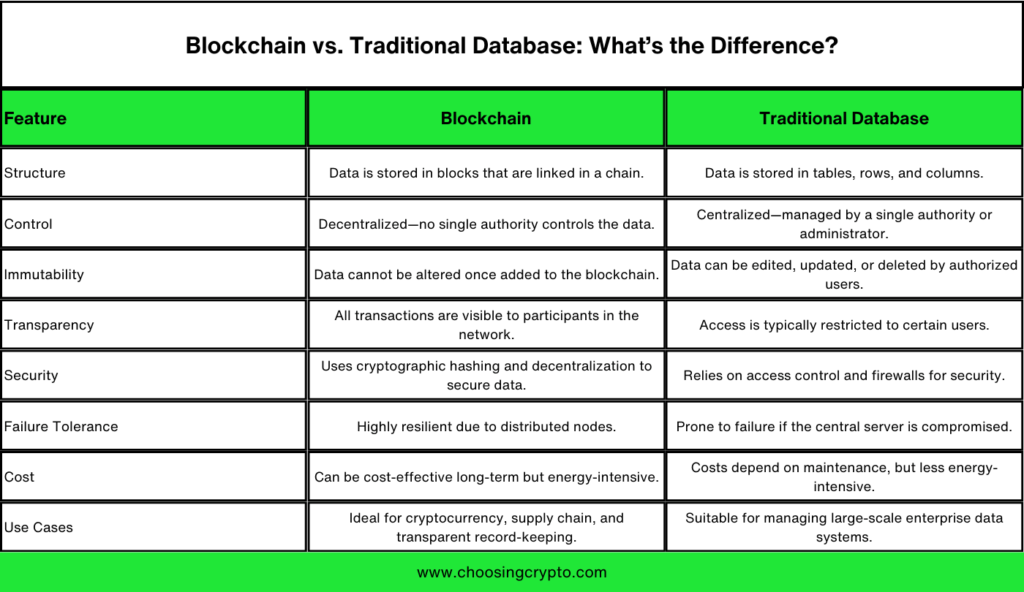
Comparing these two systems reveals how blockchain unlocks new opportunities. It’s especially powerful in areas where trust, transparency, and decentralization matter most.
Types of Blockchains
Blockchain technology is a powerful tool with different types tailored to specific needs. Here’s a simple guide to the three main categories:
1. Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to everyone. You can join as a participant, miner, or validator without restrictions. These networks are fully transparent, meaning all data is visible to users. They use consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to secure the network and validate transactions. Public blockchains are ideal for cryptocurrencies and applications that thrive on decentralization and transparency.
2. Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are restricted to authorized users within a controlled network. Their access is restricted, making them perfect for organizations needing enhanced security and privacy. For example, businesses use private blockchains to track their supply chains, ensuring secure and efficient monitoring of goods from production to delivery. If managing sensitive data is your priority, private blockchains are a great solution.
3. Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains combine the best of public and private networks. They allow some data to remain public while keeping other information private. This flexibility suits organizations needing both transparency and confidentiality. A healthcare provider, for instance, might share research data publicly while protecting patient records. Hybrid blockchains are ideal for balancing transparency and privacy.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing how we handle data, conduct transactions, and build trust. Its unique features make it a game-changer in today’s digital world. Below, discover how blockchain benefits individuals and businesses.
Benefits for Individuals
- Preventing Fraud: Blockchain’s tamper-proof design ensures secure, transparent transactions. It lowers risks like online fraud and identity theft, giving users confidence in managing digital assets.
- Ownership and Control: Blockchain lets you take full control of your digital assets and data. For example, cryptocurrency wallets allow you to manage your funds independently, as private keys stay solely with you.
- Lower Costs: By cutting out intermediaries like banks, blockchain reduces transaction fees. Sending money internationally through blockchain is often cheaper, making financial services more accessible.
- Financial Inclusion: Blockchain provides financial tools for people without traditional bank accounts. With just a smartphone, individuals in remote areas can send, receive, and store funds securely.
Benefits for Businesses
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain’s shared ledger system allows businesses to track and verify every step in their operations. This transparency builds trust and accountability, especially in supply chains.
- Cutting Costs: Automating processes with blockchain reduces operational expenses. Real estate firms, for instance, can streamline transactions and minimize reliance on brokers and lawyers.
- Improved Security: Blockchain protects data with encryption and decentralization. This makes sensitive business information less vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Faster Transactions: Blockchain eliminates delays common in traditional payment systems. Instant transactions improve cash flow and fix inefficiencies in financial operations.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers exciting possibilities, but it also faces significant challenges. Understanding these issues is crucial for anyone interested in blockchain applications or investments. In the following, I’ll break down the key challenges in simple terms.
1. High Energy Consumption
Some blockchain networks, especially those using Proof of Work (PoW), require massive energy. PoW secures the network by solving complex puzzles, but this process uses as much electricity as entire countries. Bitcoin mining, for instance, has drawn criticism for its environmental impact. Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanisms, which require significantly less energy, are addressing these concerns.
2. Scalability Issues
Blockchain networks struggle to handle many transactions quickly. Bitcoin, for example, processes about seven transactions per second, leading to delays and high fees during peak times. This low efficiency is being addressed by solutions like Solana, which processes over 60,000 transactions per second, making it a key player in improving scalability and transaction speed.
3. Regulatory Uncertainty
Global regulations around blockchain and cryptocurrency remain unclear. Some countries ban cryptocurrencies outright, while others impose strict rules that stifle innovation. This legal ambiguity makes businesses and investors hesitant, slowing the technology’s growth.
4. Irreversible Transactions
Blockchain records are permanent. This feature enhances security but leaves no room for error. Sending cryptocurrency to the wrong address, for instance, means the funds are lost forever. Users must double-check details to avoid costly mistakes.
5 Complexity and Accessibility
Blockchain can be hard to understand. Concepts like wallets, private keys, and consensus algorithms confuse many people. For newcomers, setting up a wallet or using a blockchain app feels overwhelming. Simplified tools and better education are essential to make blockchain more accessible.
Applications of Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain is most famous for powering cryptocurrencies, but its applications go far beyond digital currencies. With features like transparency, security, and decentralization, blockchain is reshaping industries and creating new opportunities. Let’s explore its top use cases:
1. Healthcare
Blockchain can revolutionize healthcare by securing patient data. Medical records stored on a blockchain ensure accuracy, improve access, and streamline processes. For example, healthcare providers can instantly verify prescription histories, reducing medical errors and saving lives.
2. Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, blockchain boosts transparency and accountability. Businesses can trace products from origin to delivery, ensuring ethical sourcing. Walmart, for instance, uses blockchain to track produce, quickly identifying and removing contaminated items.
3. Identity Verification
Say goodbye to identity theft with blockchain’s tamper-proof digital identity solutions. These solutions simplify tasks like opening bank accounts and online voting. Estonia’s e-Residency program is a prime example of secure, blockchain-backed digital identities in action.
4. Intellectual Property Rights
Creators can safeguard intellectual property using blockchain. It records ownership and timestamps for works, benefiting artists, writers, and musicians. Musicians, for example, can manage royalties directly without intermediaries, ensuring fair compensation.
5. Real Estate
Blockchain simplifies buying and selling property by eliminating intermediaries. Transparent, tamper-proof property records make verifying ownership faster and more reliable. Fraud risks drop, and paperwork becomes a thing of the past.
6. Voting Systems
Blockchain enhances election security by recording each vote as a unique, unchangeable transaction. It ensures transparency and prevents fraud. Countries like Estonia and Switzerland have successfully tested blockchain-based voting systems.
7. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs revolutionize digital ownership. Artists and creators can sell digital art, virtual real estate, and other assets directly. Blockchain platforms let them retain control until transactions are completed, ensuring authenticity.
8. Education
Blockchain transforms how academic credentials are verified. Universities can issue tamper-proof digital certificates, making it easier for job applicants to share verified qualifications with employers. Say goodbye to paper documents.
9. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate processes and enforce agreements across various sectors. For supply chain management, they ensure payments are released only after goods are delivered and verified, reducing disputes and delays. In healthcare, smart contracts can streamline insurance claims by automatically verifying conditions and processing payments. Meanwhile, in real estate, they handle transactions securely by transferring funds only after ownership is verified on the blockchain, minimizing fraud and cutting out intermediaries.
10 Charity and Philanthropy
Blockchain ensures donations reach their intended recipients. Donors can track contributions in real time, building trust in charitable organizations. Platforms like Binance Charity Foundation show how blockchain brings accountability to philanthropy.
Want personal help with crypto? I offer 1-on-1 coaching, and your first session is free. Book your free session here.
Additional Resources:
- Top 7 Blockchain Myths and Misconceptions to Stop Believing
- What Are Altcoins in Crypto? A Beginner’s Guide
- How to Start Investing in Cryptocurrency as a Beginner
- How to Become Successful in Crypto Market
And guess what? We’re also on Instagram and Twitter(X). Join us there for even more fun and useful content!

DISCLAIMER:
The information provided here is for informational purposes only. Do not rely solely on it for making investment decisions. It is not financial, tax, legal, or accounting advice. Always do your own research or consult a financial advisor before investing in cryptocurrency.
